What is metadata? It is a question many people overlook, yet it plays a crucial role in how digital files are identified, organized, and understood. Behind every photo, video, document, or webpage lies information that explains its purpose, origin, and structure. This article breaks down metadata types, real-world uses, management tools, and why it matters for everyday users.
Part 1. The Core Concept - Data vs. Metadata
The Data
Many images that people have are also pixel data. Pictures like a beautiful landscape, an everyday moment, or a professional portrait. These are what most people consider a photo.
The Metadata
Data consists of the visible components of the picture, but the surrounding images and the image itself are metadata. You can consider metadata like the digital fingerprint of a photo.
Some examples of metadata include:
- The name and size of a file
- The date the file was created and modified
- Brand and model of the camera
- The type of lens, its aperture, shutter speed and the ISO
- The GPS coordinates or location data of the photo.
Part 2. Common Types of Metadata
Metadata can be broken down into three general classes:
1. Descriptive Metadata
This type of metadata query is useful for identifying and describing what an image contains. Such metadata includes, but is not limited to, titles and captions, as well as keywords and other text that is useful for efficient image retrieval and categorization.
2. Structural Metadata
This type of metadata describes how the digital objects are organized and structured, so that, for example, it describes relations between several image files or layers within a file, and how different images form part of a collection.
3. Administrative Metadata
Administrative metadata explains what needs to be done to manage and maintain digital objects of this type. This can be further subdivided into categories, and a metadata extractor can help reveal technical details, rights information, and preservation data for proper handling.
- Technical Metadata: Details about the file format, resolution, compression type, and software used.
- Rights Metadata: Information regarding copyright, usage licenses, and permissions.
- Preservation Metadata: Instructions and standards for maintaining the file over time, ensuring it remains accessible and intact.
Part 3. Metadata in Action - Real-World Examples
| Example | Common Metadata Elements | Real-World Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Image & Photo Metadata | Camera model, lens type, aperture, shutter speed, ISO, white balance, GPS location, date/time captured, keywords, captions | Sort and organize photos, track shooting conditions, apply batch edits, verify copyright ownership, and auto-group photos by location/date in gallery apps |
| Video Metadata | Frame rate, resolution, codec, bitrate, audio tracks, subtitles, chapter markers, creation date, tags/keywords | Manage and search large video libraries, enable accurate playback on different devices, improve editing workflow, and enhance content recommendations on streaming platforms |
| Website & SEO Metadata | Title tags, meta descriptions, keywords, alt text, structured data, canonical tags | Boost search engine ranking, improve click-through rates, enhance accessibility for visually impaired users, and help search engines better understand website content |
| Document & File Metadata | Author name, creation/modification date, file format, version number, editing history, access permissions, classification tags | Track document changes, maintain version control, secure sensitive files, organize large archives, and enable fast file retrieval through search |
| Show MoreShow Less | ||
Part 4. How to View and Manage Metadata
Editing and analyzing the information embedded in your files becomes much easier if you use professionally designed tools to manage and evaluate such information. I present you with two reliable information management tools in the form of metadata viewers, how you can operate them on different file types, and how Tipard Video Converter Ultimate enables you to easily manipulate, even modify, and fine-tune metadata concerning media files.
Reliable Metadata Viewers
1. ExifTool (Windows, macOS, Linux)
Among the most prominent command-line interfaces is ExifTool, which allows users to view metadata and read/write virtually all forms of metadata standards, such as EXIF, IPTC, XMP, and ID3. It is popular in photography, archiving, and research, and widely sought for in-depth record analysis.
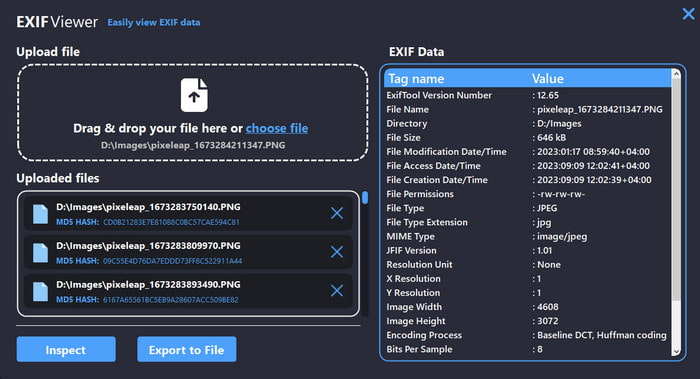
What it can display:
- Details regarding your camera (aperture, ISO, focal length, shutter speed)
- Coordinates of GPS
- Times and Dates
- Copyright details
- Technical information on Video/audio files
2. Adobe Bridge (Windows & macOS)
In case you prefer to use a graphic interface, Adobe Bridge is an excellent alternative. It is an image, video, and document metadata viewer and is excellent for file collection aid.
What it can display:
- Description of files and keywords
- Details of Photographers
- Camera/lens details
- Copyright & licensing
- Properties of the document
- Documents the attributes as thumbnails for easy and quick access and navigation.
Advanced Metadata Editor: Tipard Video Converter Ultimate
For creators needing quick and precise editing of metadata, Tipard Video Converter Ultimate offers a complete toolset. Besides converting, there is a built-in Metadata Editor that edits details of videos and audio. Currently, there is a short-term offer that provides all editing, ripping, and converting features for a fraction of the price.
- Update song titles, albums, artists, genres, and add or replace album artwork.
- Modify video titles, authors, comments, dates, and embedded descriptions.
- Select multiple files and apply changes at once to speed up media management.
- Edit metadata for almost any video or audio format, perfect for mixed libraries.
- Simple, organized tools make it easy for beginners to update file details.

Step 1 Download and Install the Tool
Visit the Tipard Video Converter Ultimate product page, click Free Download for either Windows or Mac. Open the installer and follow the instructions in the installer.
Step 2 Launch the Software
Open Tipard Video Converter Ultimate on your computer. From the top menu, select the More Tools option.

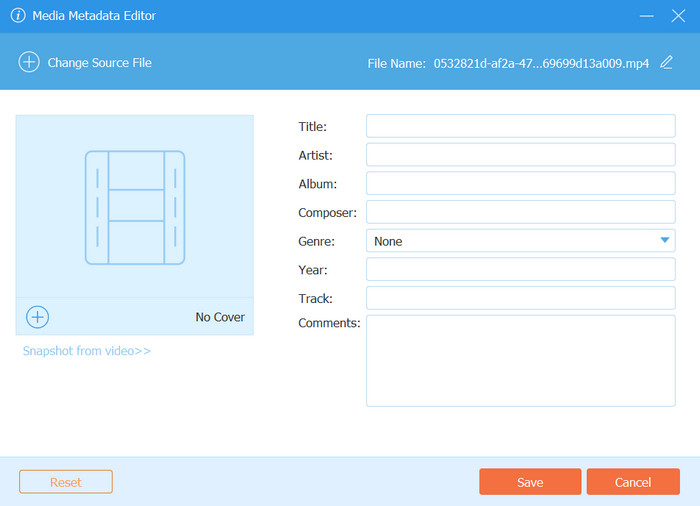
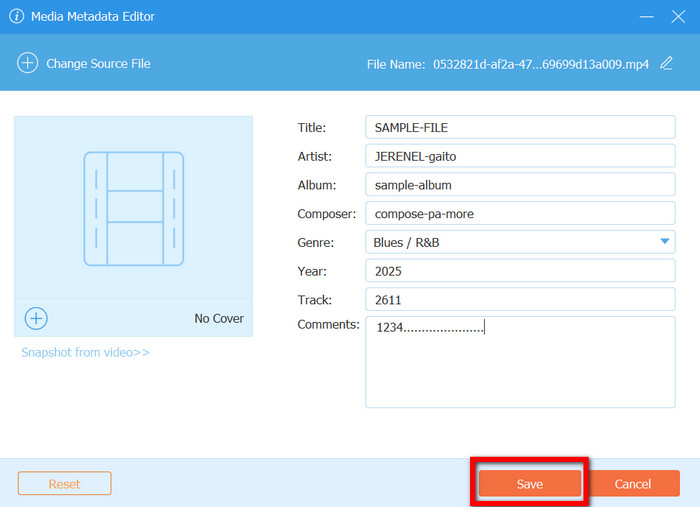
Step 3 Open the Media Metadata Editor
Look for the Media Metadata Editor and click on it. A window will pop up, allowing you to change the details inside your files.
Step 4 Add Your Video or Audio File
Click the Plus (+) button to import the media file, the metadata of which you wish to change. It will automatically search the file and show you the available metadata.

Step 5 Edit the Metadata Fields
At this point, you may change the details of the metadata, such as the following:
- Title
- Artist
- Album
- Genre
- Year
- Comments
- Cover art
- Description and file information of the video
Change the details as necessary in relation to what the file requires.
Step 6 Save Your Updated Metadata
Once done, click Save to apply the new metadata to your file. Your updated file will now contain clean, accurate, and fully customized metadata.
Part 5. Why is Metadata So Important
Organizing data in the right order is one important aspect when dealing with metadata, but an aspect that has an influence on all media converter tools is metadata. Users can keep organized media files, optimize media files to their preferences, and keep files that are input into their software in a structured format.
1. Makes File Organization Easier: With metadata, users can keep files based on the title, date, and even the category. With this type of organization, users can edit video metadata and keep their files in a more structured format, such as storing all media files in the same folder.
2. Improves Searchability and Retrieval: Users will be able to access their files more easily as the software is able to understand the content of a file and is able to put the files in the appropriate folder or even archive them into a compact file.
3. Enhances SEO and Online Visibility: Search Engines will be able to use the information in the metadata to generate a better search.
4. Ensures Proper File Identification and Context: Context is important, and with metadata, it can keep a record of who edited a file and what date it was edited. This is crucial, especially when we need information for documentation.
5. Assists with Editing, Conversions, & Playback Compatibility: The presence of audio and video metadata also allows software to detect the various codecs, frame rates, and formats for editing. Without the right metadata, files can become unopenable, sync issues can arise, and playback may result in errors.
6. Drives Automation and Smart Capabilities: To enhance, sort, and recommend various content, applications rely on metadata. Examples include:
- Recognizing locations in photo applications
- Grouping videos by date in video applications
- Sorting songs by album or artist in music applications
Conclusion
Metadata means more than just the other information about a file. It represents the essence of order, simplicity in locating a file, and precision in dealing with digital details. The proper understanding and control of metadata ensures that files are in order and can be used for long periods of time without concern. Digital libraries can be more efficient and organized with the right tools.








