Ever opened an old video and noticed it doesn't fill your screen? That's a 4:3 video. It was the standard before wide screens became common. Today, you mostly see it in old recordings, camcorder clips, or retro games. But it still matters, especially if you edit old content or work with classic displays.
This guide explains 4:3 video resolution, lists the most common formats, and compares it to today's 16:9. You'll learn what 4:3 is and how to change your video resolution without losing quality.
Part 1. What Is 4:3 Video Resolution
The 4:3 video resolution refers to an aspect ratio. This means that the screen's width is four units and the height is three units. This was the standard screen size for TVs and computer monitors before widescreen formats like 16:9 became popular.
When you see something in 4:3, you're not looking at the number of pixels yet. You're looking at the shape. The actual resolution in pixels depends on the size and quality of the screen or video, but the shape always stays the same: a bit more square than widescreen.
This aspect ratio is still standard in old videos, surveillance systems, and mobile or embedded screens. It's also used for artistic reasons when a more vintage or compact look is needed. Recording in 4:3 can also help improve Zoom video quality, especially for interviews or presentations where a centered, focused frame works better. Many Zoom recordings default to 16:9, but switching to 4:3 can reduce distractions and keep the attention on the speaker.
Part 2. List of 4:3 Video Resolution
You need the correct resolution to match if you're working with a 4:3 video ratio. The wrong one can make your video look stretched, squashed, or blurry. These are the most common 4:3 video resolutions, briefly explaining where and why they're used.
640×480 (VGA)
This is one of the oldest and most basic 4:3 resolutions. It was the default for many CRT monitors and early digital cameras. Even though it's low resolution by today's standards, it's still used for retro games, low-bandwidth video, and embedded devices.
800×600 (SVGA)
This resolution, slightly sharper than VGA, was common on school and office computers in the early 2000s. It's still found in legacy hardware and basic presentation systems.
1024×768 (XGA)
This was a popular display size for business projectors and early flat-panel monitors. It's clear enough for basic web browsing and presentations, and it's still used in some older projectors and point-of-sale systems.
1280×960
This is a high-quality 4:3 resolution that works well for detailed graphics and cleaner video playback. It's good when you want to preserve the 4:3 shape without giving up too much clarity.
1400×1050 (SXGA+)
This resolution was mainly used on high-end laptops and business monitors. It offers more vertical space than 1280×960, which is helpful for documents and spreadsheets. It's rare today, but still valid for 4:3.
1600×1200 (UXGA)
This is the highest commonly available 4:3 resolution. It offers sharp detail and is ideal for professional editing or archiving content initially shot in 4:3. You'll mostly see it in high-end vintage monitors or older scientific equipment.
1152×864
This one is tricky. It's not exactly 4:3, but it's very close. Some older graphics cards used it as a middle ground between 1024×768 and 1280×960. It may be labeled as 4:3, but it's more of a close enough option.
Part 3. Common 4:3 Ratio Calculator You Can Use
Let's say you want to create a new video in 4:3 or crop an existing one. You'll need to figure out the correct width and height. That's where aspect ratio calculators come in. They save you from doing the math every time. Here are some reliable online calculators that do this for you:
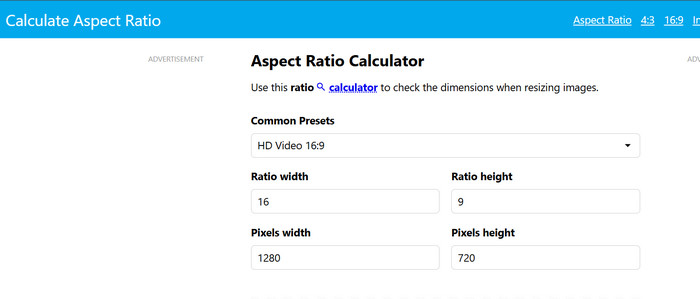
CalculateAspectRatio - Aspect Ratio Calculator
Just enter one number, and it fills in the rest. It's quick and works for both images and videos. It also has built-in presets like 16:9, 3:2, 21:9, and 4:3, which you can use for reference.
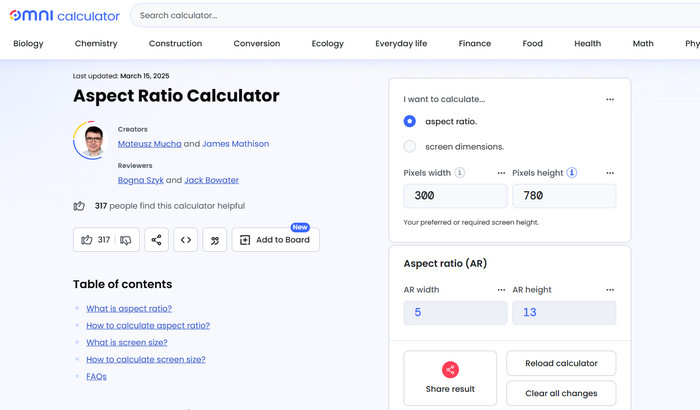
OmniCalculator - Aspect Ratio
It is better for advanced use. It gives you a live preview and lets you lock either width or height. As you type, it shows you exactly what aspect ratio you have.
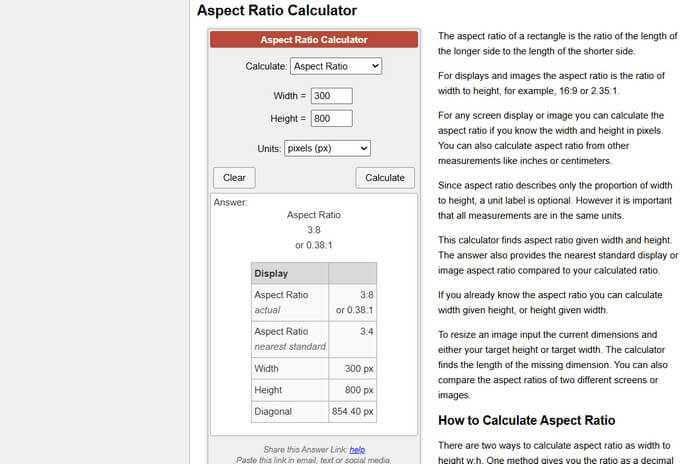
CalculatorSoup - Aspect Ratio Calculator
Simple and clear. You enter your original size and target ratio, and it tells you how to crop or scale it. It also includes details like diagonal size in pixels.
Part 4. Is 4:3 the Same as 16:9 Aspect Ratio - What's the Difference
4:3 and 16:9 aren't the same. They have different shapes and work better for different uses. 4:3 aspect ratio is closer to a square, with a taller frame. It was common on older TVs and cameras. 16:9 is broader and more stretched out. It's now the standard for phones, TVs, and streaming.
Let's break it down:
| Aspect Ratio | Used In | Shape | Best For | Downsides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4:3 | Older TVs, camcorders, CRT monitors, and old YouTube videos | Tall and compact | Retro video, interviews, talking heads, mobile vertical displays turned sideways | Black bars appear on modern screens unless adjusted |
| 16:9 | Modern TVs, smartphones, YouTube, Netflix, and video games | Wide and cinematic | Movies, tutorials, gaming content, and wide shots | Doesn't work well for very old videos |
Part 5. Change Video Resolution from 16:9 to 4:3
Some online tools mentioned in Part 3 cannot handle large video files and may simply crop the entire video without precision. You'll need dedicated software to achieve a specific aspect ratio like 4:3. Fortunately, we've found the right tool for the job.
Tipard Video Converter Ultimate is one of the top tools for customizing video resolution to your preference. It supports resolutions up to 8K and handles over 500 video formats. You can also use it to rip and copy content from DVDs and Blu-rays, which becomes editable once digitized. Its cropping feature makes it easy to resize videos to standard aspect ratios like 4:3, 16:9, and 1:1, or customize them freely. It can also increase video resolution if you want to improve the quality of larger screens. Additionally, you can adjust output settings, including format, encoder, bitrate, and other metadata.
How to Use Tipard Video Converter Ultimate:
Step 1To acquire the software, simply click the Free Download button below. Double-click the downloaded file to install it on your computer. Run the program afterward.
Step 2On the main interface, click the More Tools tab. Scroll down and select Video Cropper. Click the Plus button to upload your video, or simply drag and drop the video onto the interface.
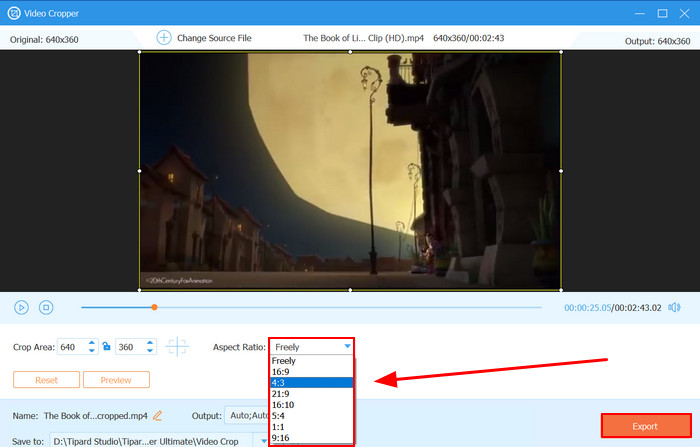
Step 3Under Aspect Ratio, click to open the list of options and select 4:3. If needed, click on Output settings to edit the video's metadata, including format, encoder, bitrate, etc. Once you're finished, click Export to save your edited video.
Conclusion
The 4:3 resolution can be ideal for specific devices or screens that support it. However, you should also consider its playability on modern devices, which may appear smaller than today's standard widescreen formats. Fortunately, with software like Tipard Video Converter Ultimate, you can freely adjust your video resolution without compromising quality.






