Choose the File System: A Comparative Analysis of FAT32, NTFS, and exFAT
FAT32 format, a file system developed by Microsoft, stands out for its compatibility and simplicity. It's commonly used for formatting USB drives, memory cards, and other portable storage devices because it works smoothly across various operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux. While newer systems like NTFS and exFAT have emerged, FAT32 remains popular due to its ability to work seamlessly across different devices and platforms. In this guide, we'll explore what makes FAT32 unique, compare it with other file systems, explain how to change the format, and provide solutions for data recovery after formatting. Join us as we discover the strengths and limitations of FAT32, how to change it, whether NTFS and exFAT are better than it, and ways to recover data after formatting to FAT32.

Part 1: Brief Comparison - FAT32 vs NTFS vs exFAT
File systems are the backbone of how data is organized and stored on our devices, significantly impacting compatibility, security, and file size capabilities. This segment delves into three prevalent file systems: FAT32 vs.NTFS vs. exFAT.
1. FAT32
FAT32, or File Allocation Table 32, is an older file system introduced by Microsoft in the mid-1990s. It's renowned for its compatibility with various operating systems and devices, making it a favored choice for USB drives, memory cards, and other portable storage.
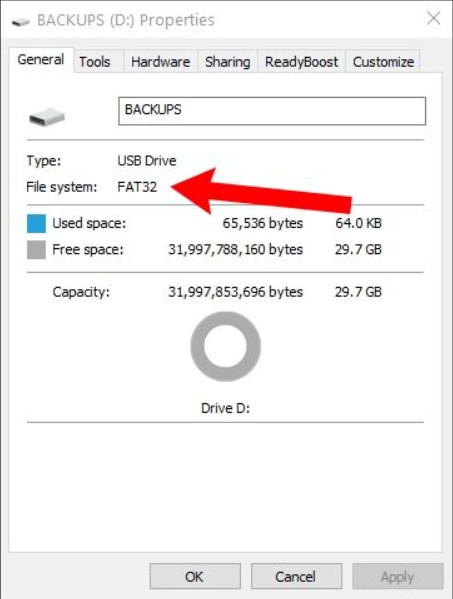
Structure:
FAT32 utilizes a file allocation table to manage and keep records of files on a storage device. It includes a boot sector, file allocation table, root directory, and data clusters.
Security:
- • It is limited.
Journaling:
- • It is absent here.
Pros:
- • Works across multiple platforms like Windows, macOS, Linux, and gaming consoles.
- • Easy to manage and access on different devices.
- • A wide range of devices supports it due to its age and simplicity.
Cons:
- • Limits file size to 4GB, restricting storage of large files.
- • Lacks modern security features like encryption and permissions.
- • The absence of journaling can lead to higher susceptibility to data corruption or loss.
2. NTFS
NTFS, also known as New Technology File System, is a robust file system developed by Microsoft with advanced features aimed at modern computing needs. It's the default file system for Windows operating systems.
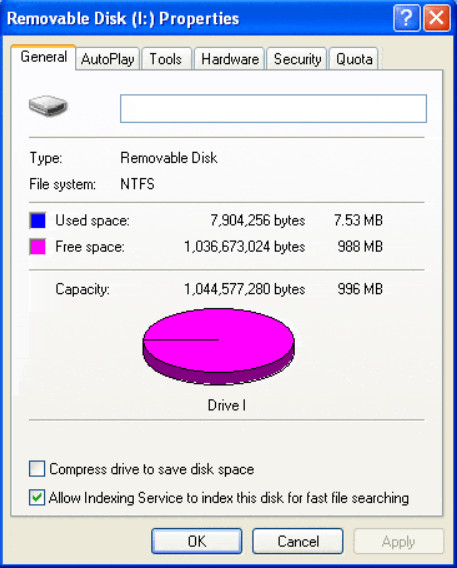
Structure:
NTFS has a more complex structure than FAT32, incorporating advanced features such as file permissions, encryption, compression, journaling, and support for larger file sizes. That is why the NTFS wins in terms of structure FAT32 vs. NTFS.
Security:
- • It is present.
Journaling:
- • It is primarily Windows-based.
Pros:
- • It supports file-level security, encryption, and compression.
- • There is no limitation on individual file sizes.
- • Incorporates journaling for improved data integrity and recovery.
- • It supports symbolic links, file permissions, and more.
Cons:
- • Native support primarily on Windows systems.
- • Advanced features might be overwhelming for casual users or particular devices.
- • Some older devices only partially support NTFS.
3. exFAT
exFAT, Extended File Allocation Table, does Microsoft develop a file system that aims to address the limitations of FAT32, particularly in handling larger file sizes. exFAT vs FAT32 clearly states the exFAT is better, but compatibility limitations are available on FAT32.
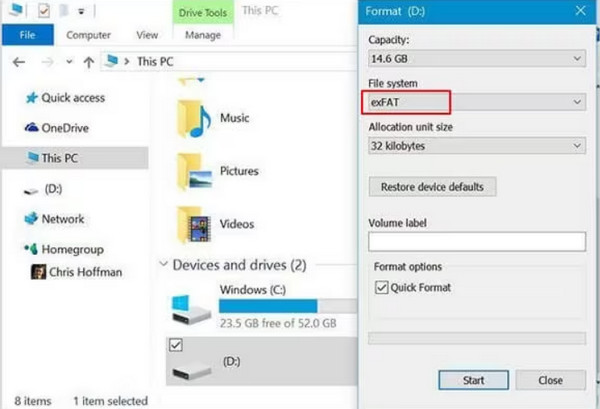
Structure:
exFAT is an extension of the FAT32 file system, designed to overcome limitations present in FAT32, particularly addressing enormous file size support while maintaining compatibility.
Security:
- • It is limited.
Journaling:
- • It is improved cross-platform.
Pros:
- • Overcomes FAT32's file size limitation, allowing for larger files.
- • It offers improved compatibility across various platforms compared to NTFS.
- • It is easier to manage and faster than NTFS for specific uses.
Cons:
- • Lacks the advanced security features present in NTFS.
- • While it supports basic forms of journaling, NTFS is more robust.
- • Compatibility might still be an issue with some devices and systems.
Part 2: How to Change the USB Flash Drive or SD to FAT32 Format
This section will guide you through formatting your USB flash drive or format SD card to FAT32 on Windows and macOS systems. However, before undertaking this process, it's highly recommended to back up any critical data stored on the device to prevent accidental loss or deletion.
On Windows:
Step 1Plug the USB flash drive or insert the SD card into an open USB port or card reader slot on your Windows computer. Hit Windows + E to start the File Explorer and locate the USB drive or SD card in the list of drives.
Step 2Right-click on the USB drive or SD card and select Format. Choose FAT32 from the File System dropdown menu in the format window that appears. You can also set the Allocation unit size and provide a Volume label if needed.
Step 3Click Start to begin the formatting process. A warning message might appear, stating that formatting will erase all data. Confirm and proceed if you're certain.
Step 4Once the format is completed, you'll receive a confirmation message. Click OK to finish.
On Mac:
Step 1Plug the USB flash drive or SD card into an open USB port or card reader slot on your Mac. Go to Applications, Utilities, and Disk Utility, or you can search Disk Utility using Spotlight.
Step 2In Disk Utility, find your USB drive or SD card from the list. Click on the drive, not the volume under it, to select it.
Step 3Click on the Erase button at the top of the Disk Utility window. Choose MS-DOS (FAT) from the Format dropdown menu. Provide a name for the drive if needed.
Step 4Click on Erase and confirm the action when prompted. Then, Disk Utility will begin erasing and formatting the USB drive or SD card to FAT32. Once the process finishes, you'll receive a confirmation to close Disk Utility.
Part 3: Recover Data After Formatting to FAT32 - Best Data Recovery App on PC
Did you need to back up your valuable data before formatting your USB flash drive or SD card to the FAT32 format? Don't worry; you can still recover your lost files. Tipard Data Recovery is a robust application designed to retrieve lost, deleted, or formatted files from various storage devices, including USB drives and SD cards. Whether you accidentally formatted your storage device or encountered data loss for other reasons, It offers a reliable solution to recover your files efficiently.
Plus, this powerful software employs advanced scanning algorithms to thoroughly search your formatted FAT32 drive, striving to recover various file types, such as photos, videos, documents, and more. Its user-friendly interface makes it accessible to users with varying technical expertise, ensuring a straightforward recovery process.
Further Reading:
Things You Should Know about UEFI and BIOS
3 Effective Methods to Log in as Administrator on Windows 7
Part 4: FAQs about FAT32 Format
Is exFAT the same as fat32?
No, exFAT is not the same as FAT32. While Microsoft developed both file systems, they have distinct differences. FAT32 is an older file system with limitations on file size, a maximum file size of 4GB, and lacks some modern features. On the other hand, exFAT was introduced to address FAT32 limitations, offering support for larger file sizes, improved compatibility across various devices and operating systems, and better resistance to file fragmentation.
What is the FAT32 max file size?
The maximum file size supported by the FAT32 file system is 4 gigabytes. This limitation means individual files cannot exceed 4GB when stored on a FAT32-formatted drive. This restriction of file size is a notable downside for users of large files, such as high-definition videos, disk images, or large software installation files.
Can I convert a drive from NTFS or exFAT to FAT32 without losing data?
Converting from NTFS or exFAT to FAT32 without losing data requires reformatting the drive, resulting in data loss; before converting, back up your data to avoid losing important files.
Which operating systems support FAT32?
FAT32 enjoys broad support across various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and many other platforms. Its broad compatibility makes it a popular choice for USB drives and memory cards that need to be accessed across different systems.
Can the file system of a drive be changed from FAT32 to NTFS or exFAT?
While FAT32 can technically be used on large external hard drives, its limitations in file size, which is a maximum of 4GB per file, might not be suitable for efficiently handling large storage capacities. Other file systems like NTFS or exFAT are better suited for large-capacity drives because they support larger file sizes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the FAT32 vs. NTFS vs. exFAT has been a hot topic for a long. As you can see, FAT32 continues to be a favored choice due to its compatibility across various platforms. However, its limitations in handling larger file sizes and security features have led to the development of alternatives like NTFS and exFAT. Understanding the differences among these file systems aids in making informed decisions when choosing the right format for specific storage needs.







